What Is Posterior Tibial Tendinopathy?
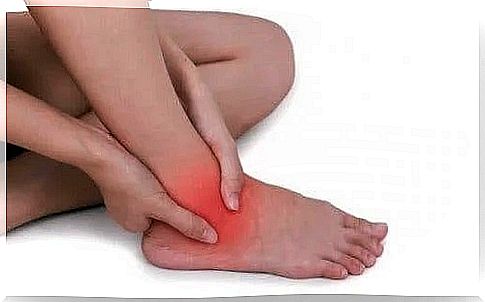
Posterior tibial tendinopathy is a tendon injury that causes pain and inflammation and limits movement. The tendon affected in this pathology is found in the posterior tibia, which is fundamental in the functioning of the ankle and foot.
The posterior tibia is an elongated muscle of the leg, located at the level of the leg. The muscle is inserted on the tibia, fibula and interosseous membrane (which connects both bones) inside.
This muscle continues its way in the form of a tendon, passing behind the tibial ankle, which is the inside of the ankle. Then it enters the scaphoid or navicular bone, which is the upper part of the arch of the foot.
It is also inserted into the wedge-shaped bones and the three central metatarsals, the bones in the front of the foot. As you can see, the muscle and tendon occupy a large part of the leg and ankle. Therefore, their proper functioning is crucial.
What is posterior tibial tendinopathy?
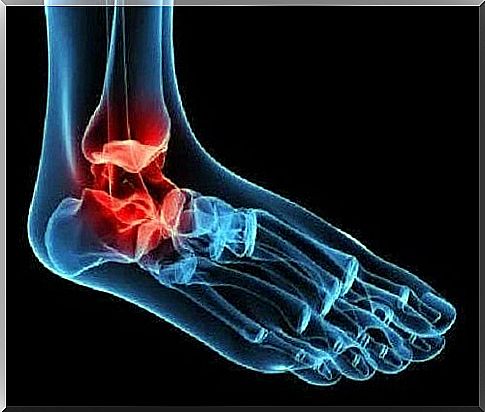
As we have already pointed out, posterior tibial tendinopathy is a lesion of the tendon of the same name. The word tendinopathy is a general term used to refer to both tendinitis and tendinosis. Therefore, when we talk about posterior tibial tendinopathy, we are referring to both types of lesions.
Tendinitis involves swelling of the tendon, while tendinosis refers to a degenerative process. However, many researchers believe that the term tendinitis is inaccurate in this case and that tendinopathy is a more appropriate term.
Posterior tibial tendinopathy causes significant limitations in the movement of the foot and ankle. This is because the posterior tibia performs important functions, such as:
Causes of tendinopathy
Posterior tibial tendinopathy is an injury that occurs as a result of excessive use of the ankle and mainly affects runners and people who walk a lot. It occurs due to anatomical and / or biomechanical factors.
Among the anatomical and biomechanical factors that lead to posterior tibial tendinopathy is excessive pronation. This is the normal inward rotation of the foot that occurs when we walk. Often, excessive pronation is the result of flat feet. This condition unjustifiably stresses the tendon.
Another anatomical factor is being overweight or having a high body mass index (BMI). Previous inflammatory diseases, neurological disorders or degenerative changes in the joints also play an important role in the development of the disease. Posterior tibial tendinopathy is more common in women over 40 years of age.
In terms of improper practices, the main causes are the use of uncomfortable footwear, excessive wear and poor walking or running techniques. Muscle weakness and lack of flexibility of the ankle muscles can influence the evolution of the disease.